Diabetic Foot Solution
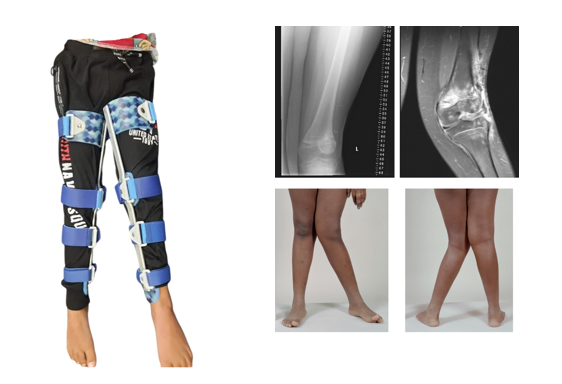
A heel ulcer is an open sore that develops on the skin of the heel, typically as a result of prolonged pressure or friction on the area. Heel ulcers can be painful and may take a long time to heal, especially in individuals with poor circulation or diabetes.
There are several factors that can contribute to the development of a heel ulcer, including:
Prolonged pressure on the heel due to immobility or sitting or lying down for extended periods of time
Friction from ill-fitting shoes or socks
Poor circulation, which can lead to slow healing and an increased risk of infection
Diabetes, which can cause nerve damage and reduce sensation in the feet, making it more difficult to detect and treat ulcers
Treatment for a heel ulcer typically involves relieving pressure on the affected area and keeping the wound clean and protected. This may involve the use of specialized dressings, pressure-relieving devices, and wound care techniques. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove damaged tissue or correct underlying structural problems in the foot or ankle.
Prevention is key in avoiding heel ulcers. This can involve regular foot inspections, wearing well-fitting shoes, and maintaining good blood sugar control in individuals with diabetes.
Price: 0 |
Payment Type: |
Available: False |
COD Available: False |
KYC Status: FAILED
Send Message