Orthosis
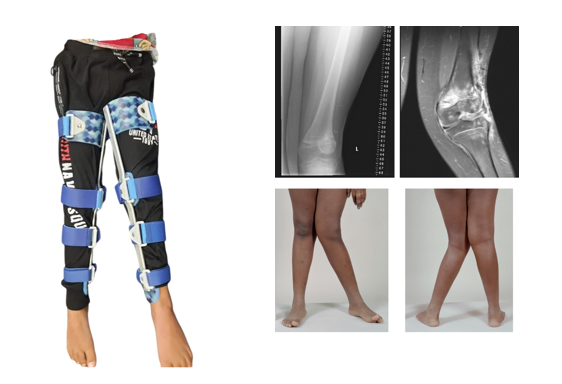
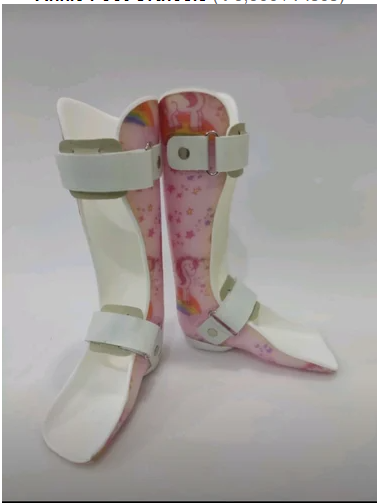
A static ankle-foot orthosis (AFO) is an orthopedic device designed to support, align, and improve the function of the ankle and foot. Unlike dynamic AFOs, which allow for movement, static AFOs are rigid or semi-rigid and provide fixed support to maintain the position of the foot and ankle.
Key Features
Design and Materials: Static AFOs are typically made from materials such as plastic or carbon fiber. These materials create a sturdy framework that is custom-molded to the individual's foot and leg, ensuring a proper fit and maximum support.
Purpose: The primary goals of a static AFO are to correct or prevent deformities, provide stability, and relieve pain. They are commonly used to manage conditions such as:
Drop Foot: A condition where the foot cannot be lifted properly, making walking difficult.
Cerebral Palsy: A disorder characterized by muscle stiffness and control issues that affect gait and foot positioning.
Stroke: To assist with walking by supporting the affected leg and foot.
Post-Surgical Recovery: To immobilize the ankle and foot after surgery, promoting proper healing.
Components:
Footplate: Covers the sole of the foot and provides essential support.
Calf Strap: Secures the AFO to the leg, usually adjustable for comfort.
Padding: Often lined with foam or other cushioning materials to enhance comfort and prevent skin irritation.
Benefits
Improved Function: Helps individuals maintain or enhance their walking ability by keeping the foot in a functional position.
Injury Prevention: Reduces the risk of falls and injuries by stabilizing the foot and ankle.
Deformity Management: Prevents or corrects deformities by maintaining proper alignment of the foot and ankle.
Fitting and Customization
For optimal effectiveness, static AFOs are custom-fitted to each individual. This usually involves taking precise measurements or molds of the foot and leg to ensure the device supports the unique anatomical structure and needs of the user.
In summary, a static AFO is managing various foot and ankle conditions by providing fixed support and alignment. Its success depends on a proper fit and regular use, making it an essential component of many orthopedic and rehabilitation strategies.
Address:
House NO -27, Gita Nagar, Society, Opposite Sanghvi Tower, Adajan Rd, Adajan, Surat, Gujarat 395009
Flat no. 1, Laxmi Mahal Apartment, 2163, near Neelayam Theatre, Sadashiv Peth, Pune, Maharashtra 411030
Plot No 17, 40, Rajdanga Sarat Pk Rd, near MEGHALAYA HOUSE, next to Pearl dental clinic, Shantipally, Block-BA, P.S:, Kasba, Kolkata, West Bengal 700107
46, Mona Shopping Center,, Andheri West,, near Navrang Theater, Mumbai, Maharashtra 400053
9377466476,8128996476
evolution healthcarepvt ltd
Send Message